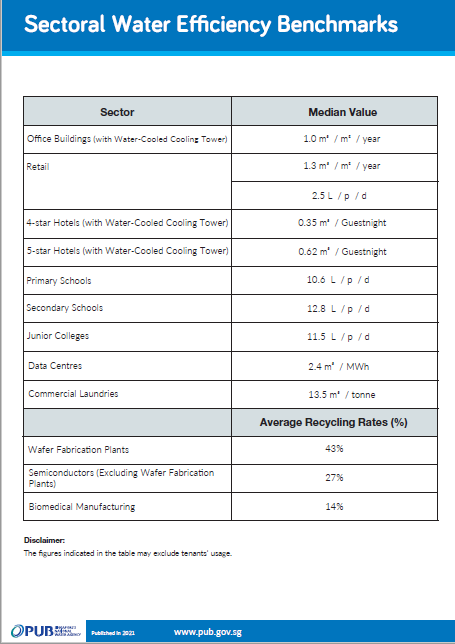
Sectoral Water Efficiency Benchmarks
The sectoral water efficiency benchmarks are tabulated based on annual water consumption data.
Download PDF >>
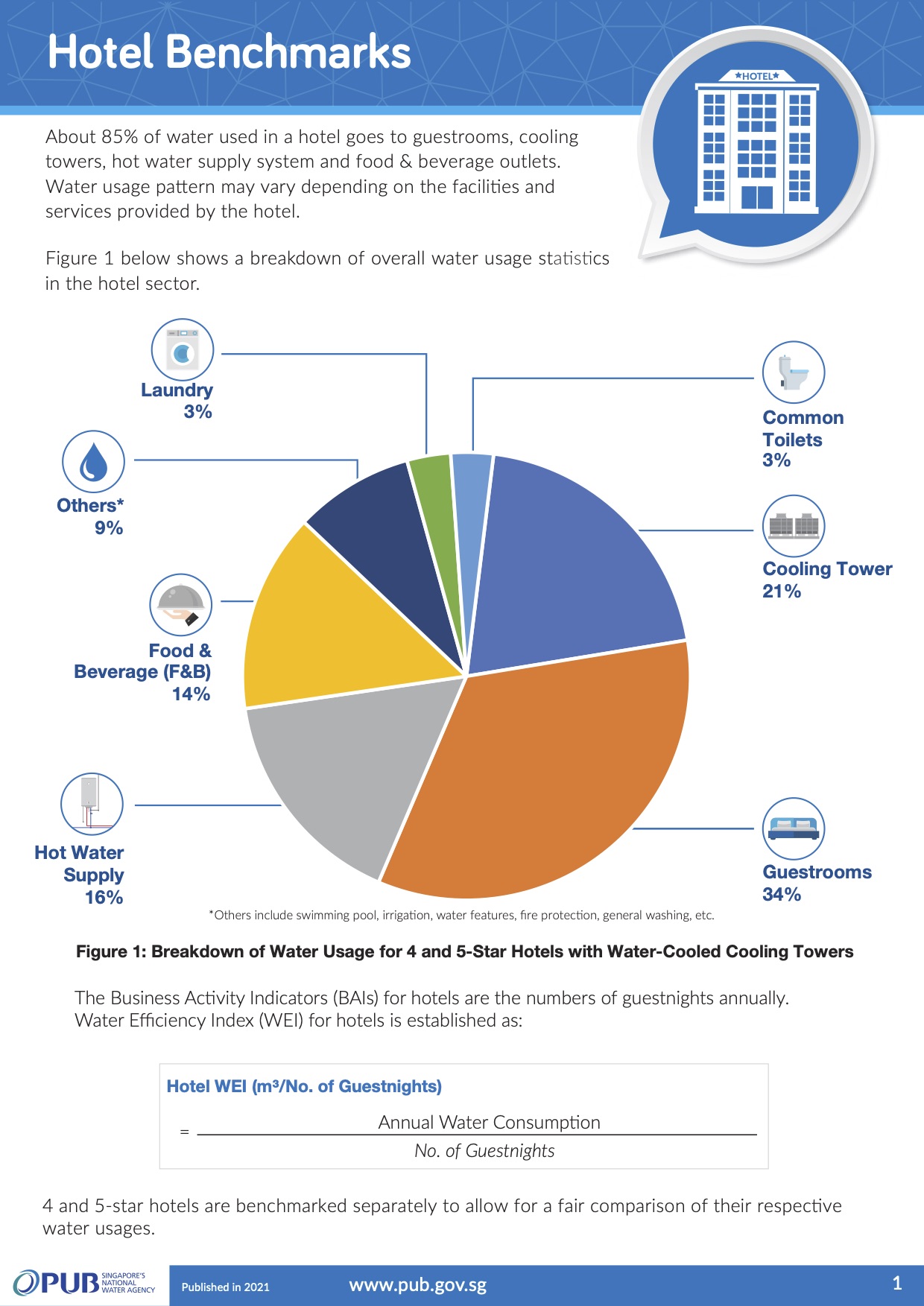
Hotel benchmarks
For the hotel sector, the Water Efficiency Index (WEI) is computed using the annual water consumption of a hotel divided by number of guestnights in the same year. This index reflects the daily amount of water a hotel used for its operations per guest.
For more details, please download the brochure below [PDF].
Download PDF >>
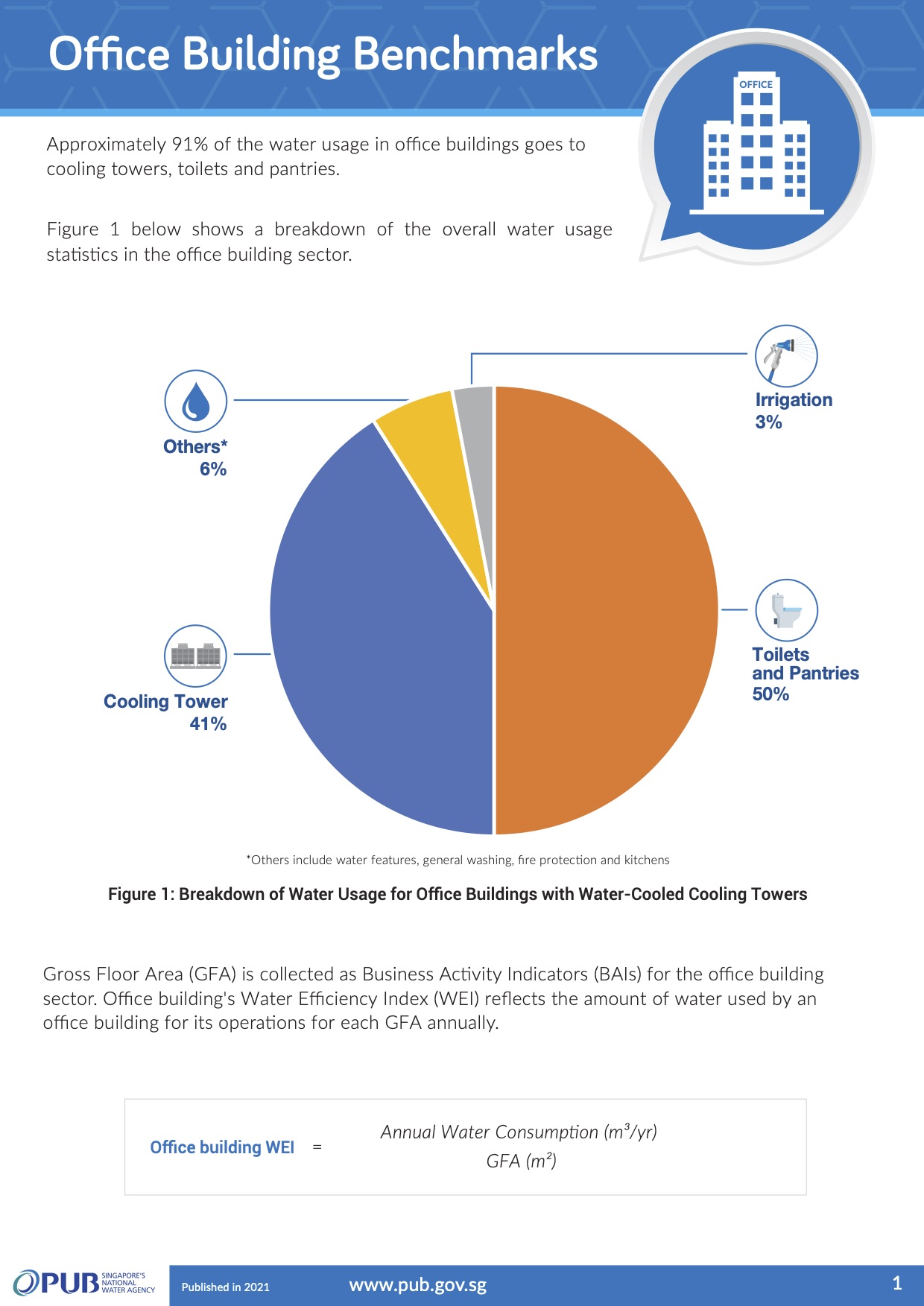
Office building benchmarks
For the office building sector, the Water Efficiency Index (WEI) is computed using a building's annual water consumption divided by its gross floor area of the building. This index reflects the amount of water used for its operations for each gross floor area annually.
For more details, please download the brochure below [PDF].
Download PDF >>
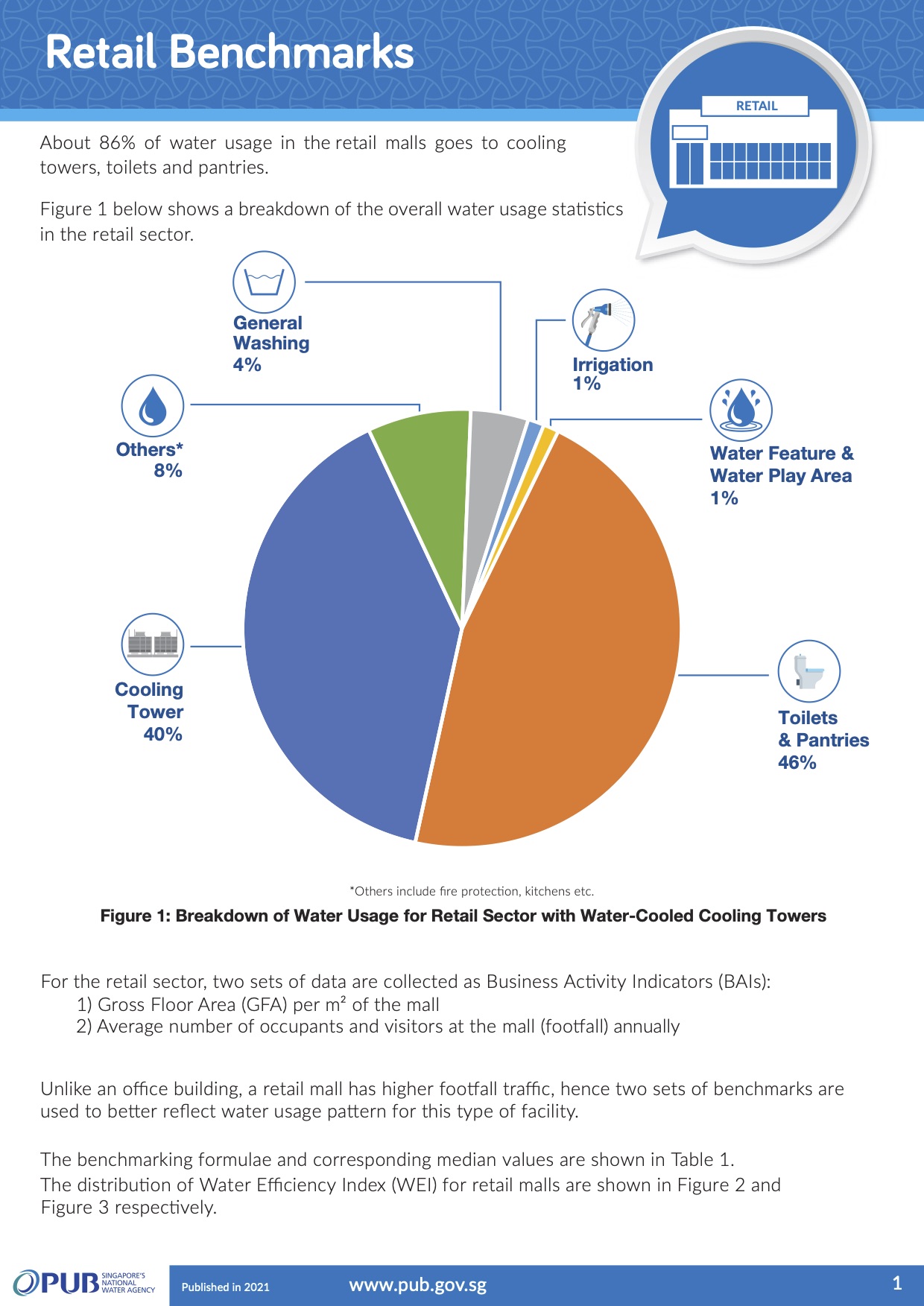
Retail benchmarks
For the retail sector, the Water Efficiency Indexes (WEIs) are computed using:
1. Annual water consumption (exclude toilets) divided by the gross floor area of a retail mall, reflecting its usage for operations per gross floor area annually.
2. Annual water consumption of toilets in a retail mall divided by the number of shoppers and days in the same year, reflecting the amount of water used per shopper daily.
For more details, please download the brochure below [PDF].
Download PDF >>
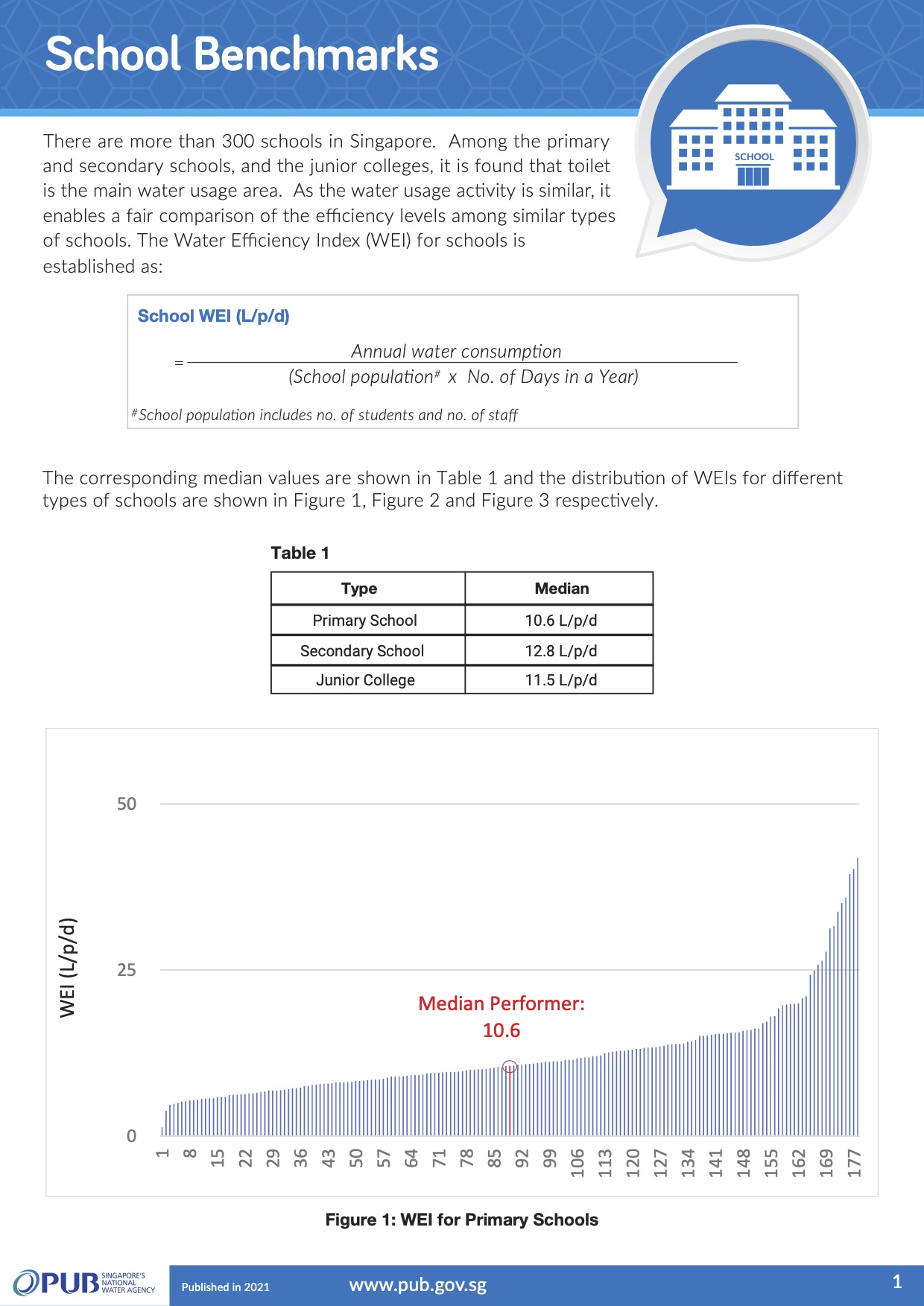
School benchmarks
Based on data collected from about 300 educational institutions (primary and secondary schools, as well as junior colleges), it was found that toilets are the main water usage areas.
For more details, please download the brochure below [PDF].
Download PDF >>
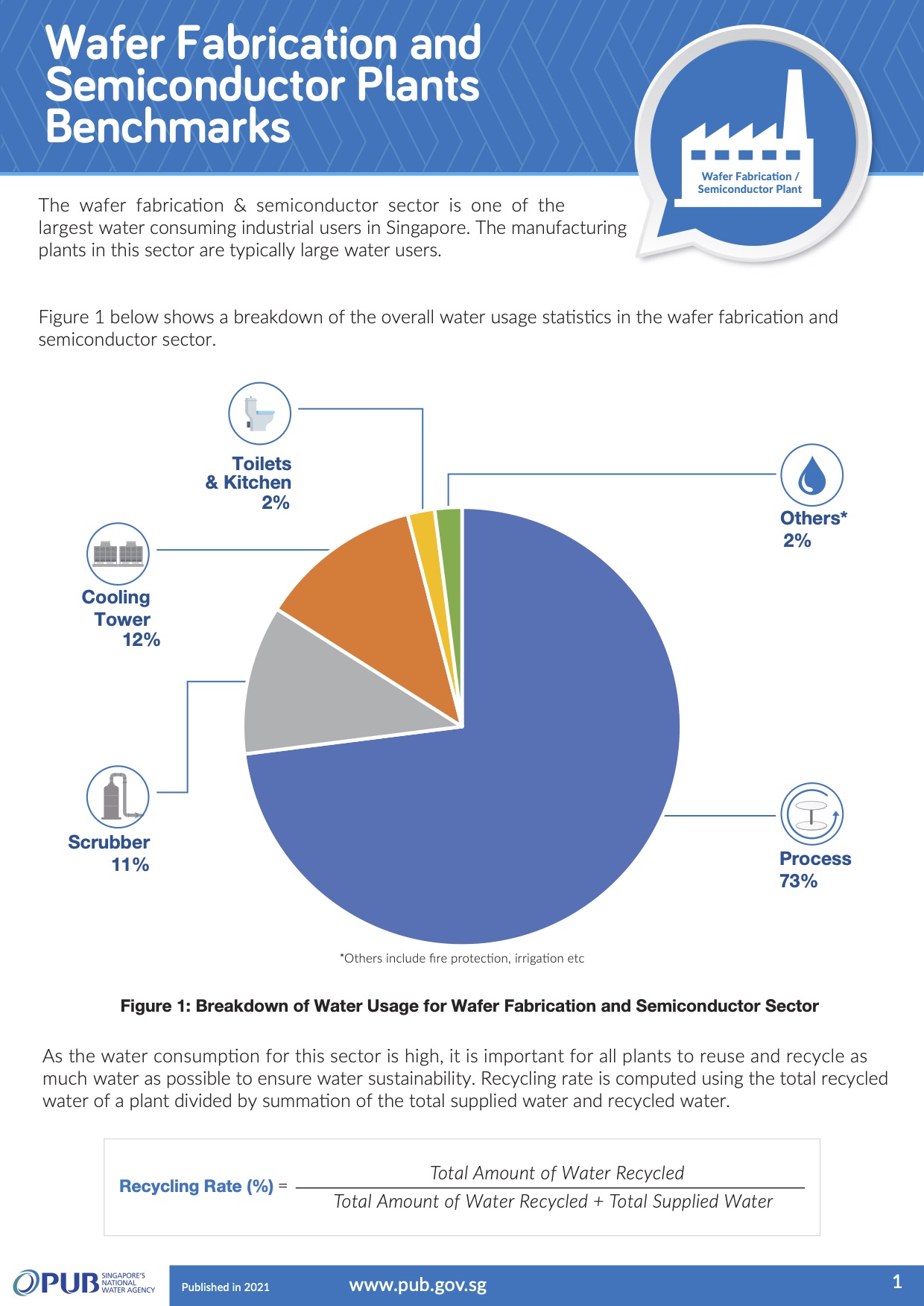
Wafer fabrication and semiconductor plants benchmarks
For the wafer fabrication and semiconductor plants sector, the recycling rate is computed using the total recycled water of a plant divided by summation of the total supplied water and recycled water.
For more details, please download the brochure below [PDF].
Download PDF >>
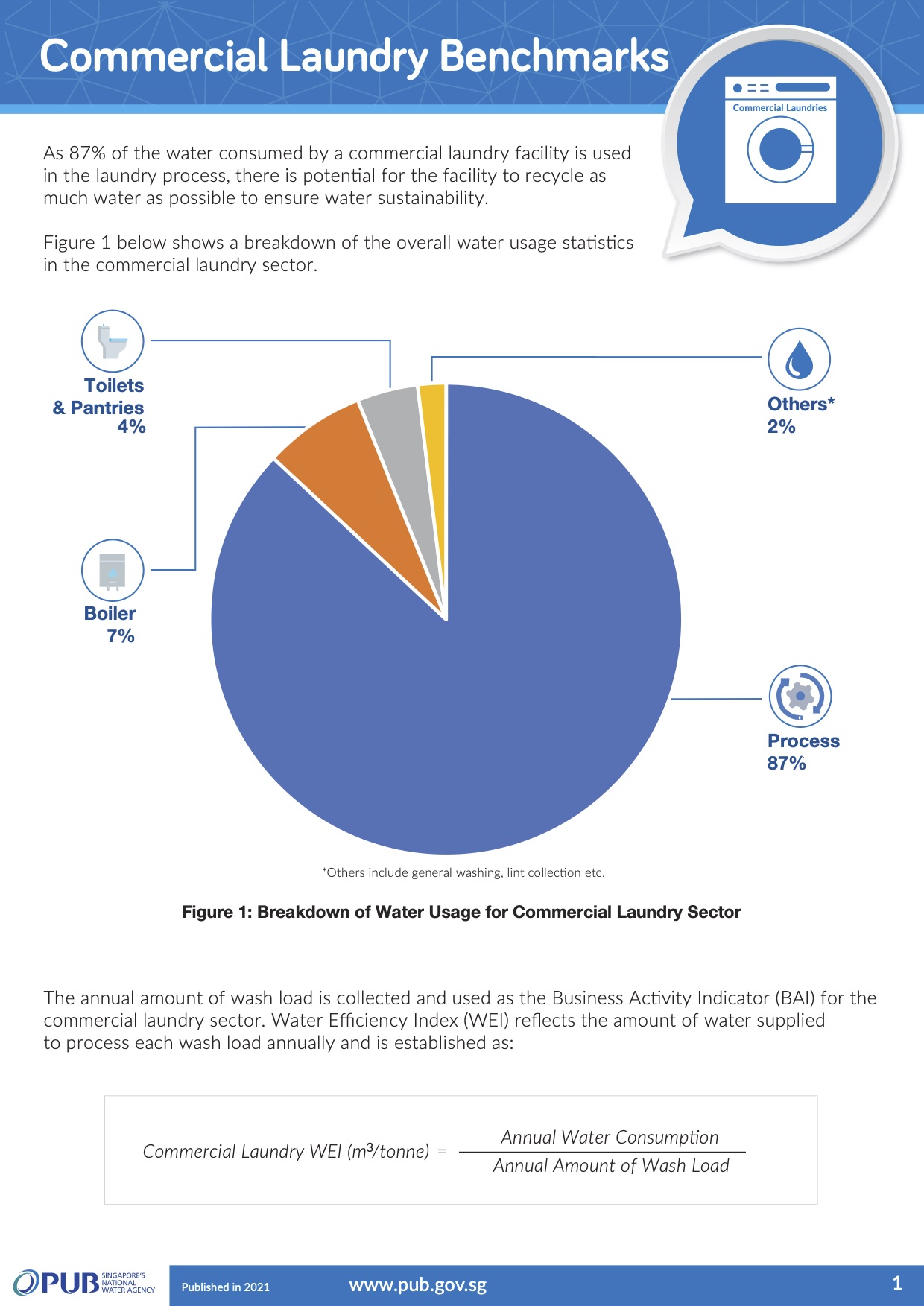
Commercial Laundry Benchmarks
For the commercial laundry sector, the Water Efficiency Index (WEI) is computed using the annual water consumption divided by the annual amount of wash load processed by the commercial laundry. This index reflects the amount of water a commercial laundry uses to process each wash load annually.
For more details, please download the brochure below [PDF].
Download PDF >>
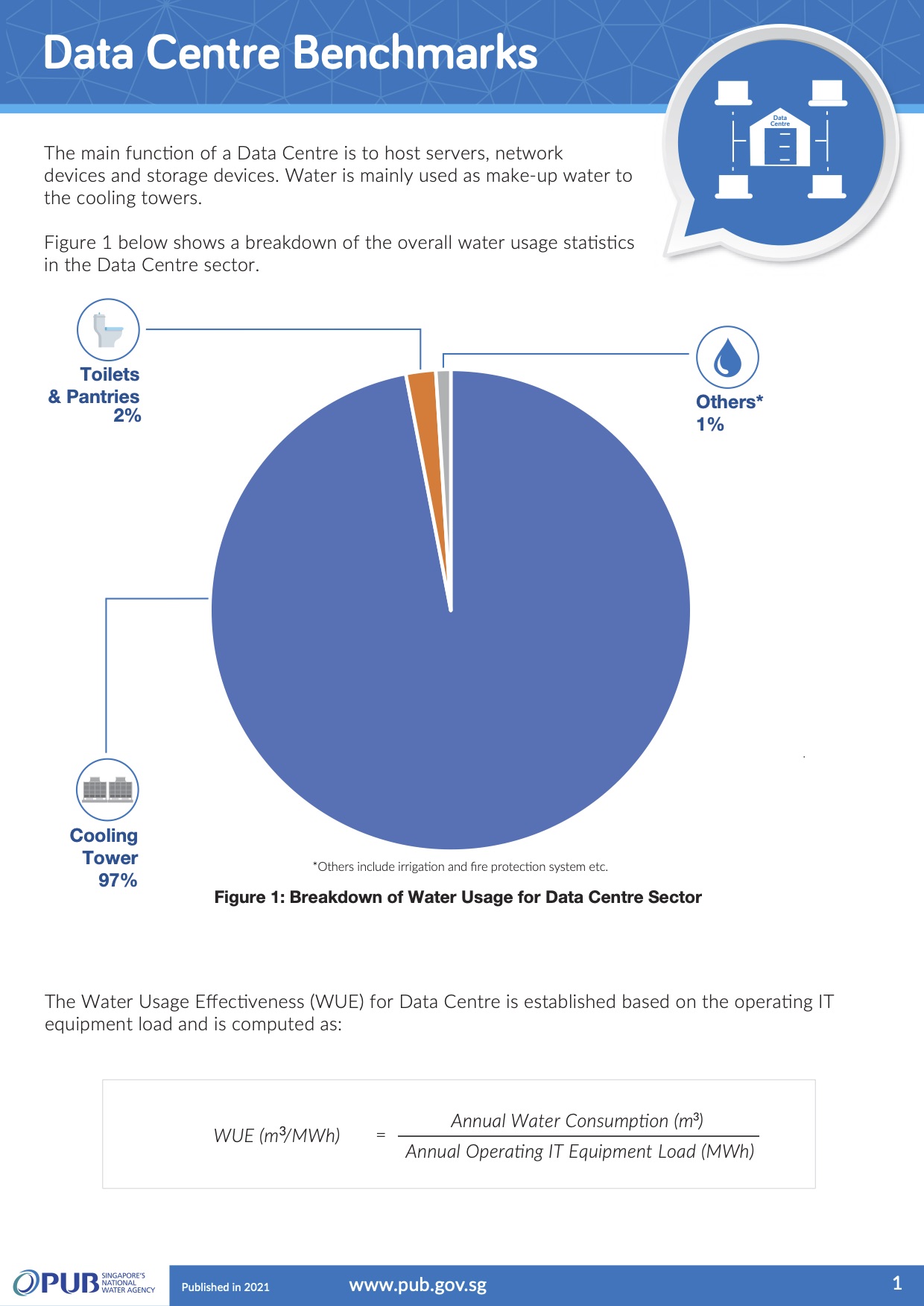
Data Centre Benchmarks
For the data centre sector, the Water Usage Effectiveness (WUE) is computed using the data centre’s annual water consumption divided by the annual operating IT equipment load.
For more details, please download the brochure below [PDF].
Download PDF >>
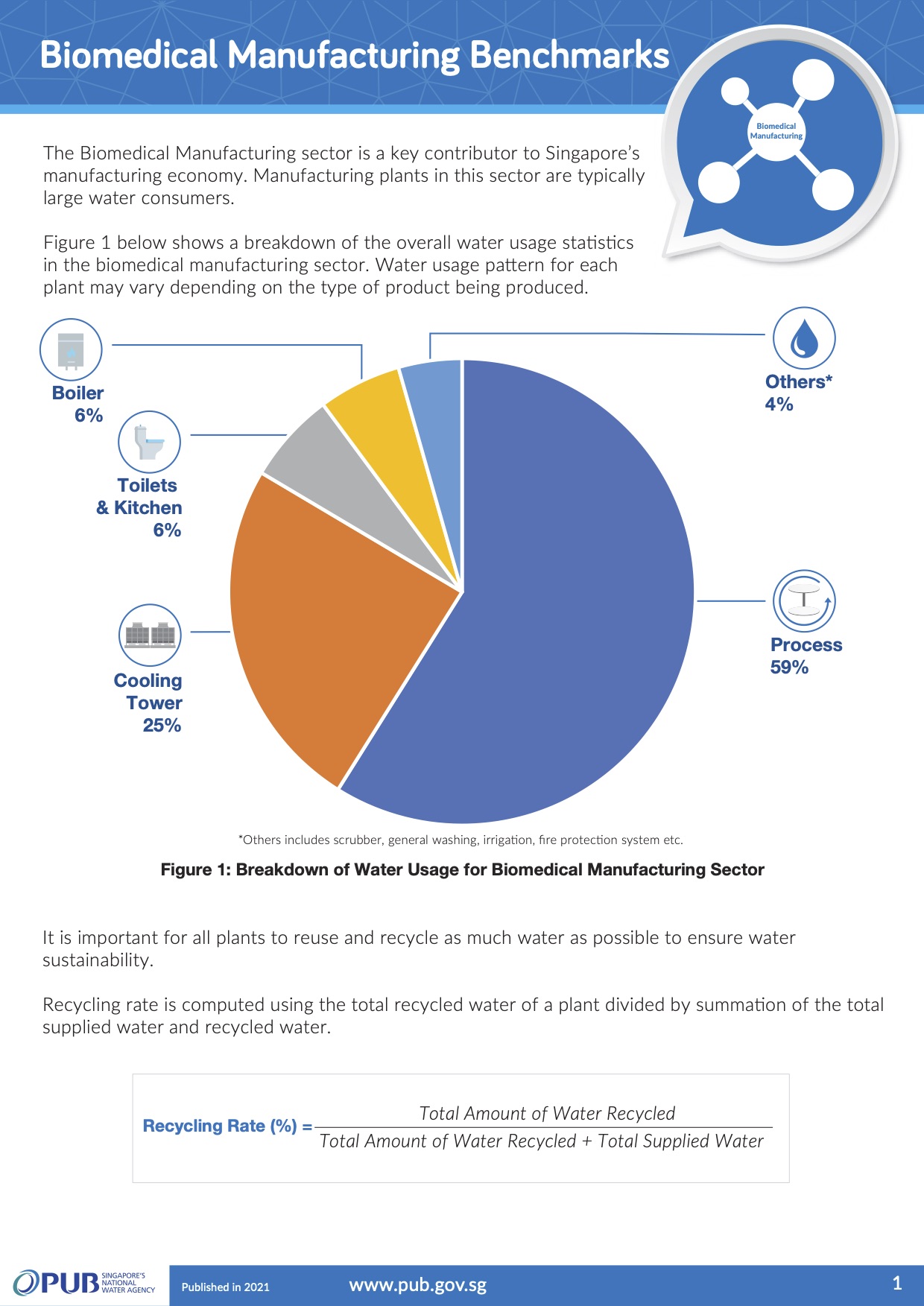
Biomedical Manufacturing Benchmarks
For the biomedical manufacturing sector, the recycling rate is computed using the total recycled water of a plant divided by summation of the total supplied water and recycled water.
For more details, please download the brochure below [PDF].
Download PDF >>